Happy Thanksgiving!!!
2016/11/24
2016/11/23
2016/07/29
Free Windows 10 Upgrade Finish Today

The idea is that Windows will be away from being a monolithic product with periodic major releases to a product that is continually updated and tweaked, in a similar a model how iOS, OS X are updated.
This idea is in line with new trends in the area of IT, where no longer the money is generated by selling software, and it is provided for “free” as a support tool for a service provided. This business model is already implemented by huge companies like Oracle, Google, etc. who provide the software for free to the average costumer and charge to companies or to everyone who need “advanced features” as an especial or premium service with a recurrent maintenance fee.

Until today Windows 10 will be offered free of charge to Windows 7, Windows 8.1, and Windows Phone 8.1, but the questions remain about the long-term implementation or this model, will be a pay-per-device, a yearly contract, pay per premium services or goods or some hybrid?
Julian Bolivar-Galeno is an Information and Communications Technologies (ICT) Architect whose expertise is in telecommunications, security and embedded systems. He works in BolivarTech focused on decision making, leadership, management and execution of projects oriented to develop strong security algorithms, Artificial Intelligence (AI) research and its applicability to smart solutions at mobile and embedded technologies, always producing resilient and innovative applications.
Free Windows 10 Upgrade Finish Today
2016/06/10
We Support to the Bill to Adjust the Immigration Status of Certain Venezuelan Nationals who are in the United States (HR3744) / Nosotros Apoyamos la Ley para el Ajuste el Estatus de Algunos de los Venezolanos que están en los Estados Unidos (HR3744)
Sometimes we need to see beyond our comfort zone and see our environment because it always affects us, and this is one of this cases; when we need to go away from our technological vision and watch in this case a humanitarian and political situation that is affecting the Venezuelans around the world and in this specific case those who live in the United States.
Many Venezuelan people living in United States are going out of a migratory status because his VISAS (H1B, F1, etc.) are expiring and forced to remain because can’t return to our country because our lives are in jeopardy due to the constant violation of the most basic human rights. This HR3744 act is not political, is humanitarian to help this people which are being helpless to fend for themselves without resources to work and to subsist.
This bill was sponsored by the Representatives Carlos Curbelo, Alan Grayson, Ileana Ros-Lehtinen, Debbie Wasserman Schultz, Patrick Murphy, Albio Sires.
This bill is supported by many no profit organizations (NPO) like Asociación de Madres y Mujeres Venezolanas en el Exterior (AMAVEX), Organización Avenext, Venezolanos En Georgia and other Venezuelan NPO around US.
For the international audience, the actual situation in Venezuela is a progressive and undercover dismantling of the democratic structure in the country started by the Lieutenant Colonel Hugo Chavez Frias in 1999 until his dead in 2013 and continued by the actual president Nicolas Maduro and always with the Engineer Diosdado Cabello’s support, among many others; and to remain in the head of the government they are throttling the Venezuelan people because they keep a strong control over the most basic resources like food, electricity, water, etc. and with this keeping the people only care how to survive the next day; and also they created and support paramilitary groups to attack anyone who dares to dissent or protest against government. In the simple way, it is a dictatorship with democratic mask.
Only 4 days left and 36000 for signing, please support the HR3744 act, you don’t need to be Venezuelan, everyone can help, just need your name and one email, and something really important is confirm your sing just clicking on the link that you will receive at your email’s inbox.
And for the people living in Venezuela, please help us to allow us help you, because we are living in other countries but we not forget you, because our families remain Venezuela and they are suffering the same human rights violations every day.
The time to act is now, not for later. Sign here!!! the White House’s petitions. #JUNTOSSOMOSMAS #APOYALALEYHR3744
—————————————————————————————————————-
Algunas veces tenemos que salirnos de nuestra zona de confort y ver a nuestro entorno porque él siempre nos afecta de una u otra forma, y este es uno de esos casos donde debemos apartarnos de nuestra visión tecnológica y observar la situación humanitaria y política que está afectando a los venezolanos alrededor del mundo y en este caso específico aquellos que viven en los Estados Unidos.
Muchos venezolanos que viven en los Estados Unidos están quedando fuera de estatus migratorio porque sus visas de trabajo, estudio, etc. Están expirando y están siendo forzados a quedarse porque no pueden regresar a nuestro país porque sus vidas están en peligro por las constantes violaciones de los más básicos derechos humanos. Esta ley HR3744 no es política, es humanitaria para ayudar a estas personas que se están quedando desamparadas para valerse por ellas mismas porque no tienen los recursos que les permitan trabajar para auto mantenerse.
Esta ley está patrocinada por los representantes al congreso de los Estados Unidos Carlos Curbelo, Alan Grayson, Ileana Ros-Lehtinen, Debbie Wasserman Schultz, Patrick Murphy, Albio Sires.
Además, está patrocinada por las organizaciones sin fines de lucro Asociación de Madres y Mujeres Venezolanas en el Exterior (AMAVEX), Organización Avenext, Venezolanos En Georgia y otras organizaciones sociales venezolanas alrededor de los Estados Unidos.
Para la audiencia internacional, la situación actual en Venezuela es un progresivo y encubierto desmantelamiento de las estructuras democráticas en el país, iniciado por el Teniente Coronel Hugo Chávez Frías en 1999 hasta su muerte en el año 2013, obra que es continuada por el actual presidente Nicolás Maduro y siempre con el apoyo del Ingeniero Diosdado Cabello, ente muchos otros; quienes para permanecer a la cabeza del gobierno, están estrangulando al pueblo venezolano porque mantienen un férreo control sobre los recursos más básicos, como lo son la comida, la electricidad, el agua entre otros; de esta forma manteniendo al pueblo venezolano solo pendiente de cómo sobrevivir el siguiente día; además ellos han creado y mantienen grupos paramilitares para atacar a cualquiera que se atreva a disentir o protestar en contra del gobierno. De forma más simple, es una dictadura con mascara de democracia.
Solo faltan 4 días y 36000 firmas para que termine el plazo de recolección, por favor apoyen la ley HR3744, no necesitas ser venezolano, todos pueden ayudar, solo necesitas tu nombre y un correo electrónico, y algo sumamente importante es el confirmar su firma, para lo cual debe hacer click en el enlace que recibe en su buzón de correo electrónico.
Para la gente que vive en Venezuela, por favor ayúdennos para así nosotros poder ayudarles, porque el hecho de que vivamos en otro país no implica que los hemos olvidado, porque nuestras familias viven en Venezuela y ellos están también sufriendo las mismas violaciones a los derechos humanos todos los días.
El tiempo de actual es ahora, no es para después. Firma Aqui!!! la petición para que la Casa Blanca se pronuncie sobre esta ley. #JUNTOSSOMOSMAS #APOYALALEYHR3744
Julian Bolivar-Galeno is an Information and Communications Technologies (ICT) Architect whose expertise is in telecommunications, security and embedded systems. He works in BolivarTech focused on decision making, leadership, management and execution of projects oriented to develop strong security algorithms, Artificial Intelligence (AI) research and its applicability to smart solutions at mobile and embedded technologies, always producing resilient and innovative applications.
We Support to the Bill to Adjust the Immigration Status of Certain Venezuelan Nationals who are in the United States (HR3744) / Nosotros Apoyamos la Ley para el Ajuste el Estatus de Algunos de los Venezolanos que están en los Estados Unidos (HR3744)
2016/06/07
The Artificial Intelligence is not Voodoo

For example, before was the vaccines, organ transplants, etc. and now is the Artificial Intelligence (AI) turn. Is interesting for me with my AI knowledges and background read and watch how the people tend to provide skill and abilities to the AI that they are far away to have, and if are diabolic is more the sensationalism in the media.
Before continue I want to extend my congratulations and thank to the company DeepMind for its open policy that allows the researchers community to have access to the methodology in the algorithms that they implemented.
The AI goal is to produce algorithms that allow computers to process data, or take decision, based on the human conception of intelligence; that is far away from the popular misconception of AI’s goal is create a superior intelligence, because as was explained on the other publication “Artificial Intelligence, is really so dangerous?” we don’t understand what intelligence really is.
Examples from this devilish perception of the IA can be found so easy in the media, because it is really easy to catch the reader attention with this kind of sensationalism that provide a better understood of how is really working.

The research engineers ran various pictures through its neural network, to identify patterns in the images and then alter that image by mixing the original with the image recognized by the DNN, this makes the picture look a little bit more like the pattern that DNN recognized. The neural network then repeats the process with the altered image and after enough times, the picture change radically. At the end the Deep Dream algorithms reinforce a DNN’s false positive by mixing the pattern with the original image and running again with the modified image reinforce more the false positive.
In this algorithm is nothing mysterious, diabolic or brujeria (witchery), you can see it as any of the Snapchat’s silly filters, and you can create your own images at the Deep Dream Generator web page; but you can find media headers like “Now You Can Turn Your Photos Into Computerized Nightmares With Deep Dream” or “Deep Dream: Artificial intelligence meets hallucinations” for example, or in other cases can be worse, for example the youtuber ‘DrossRotzank’ in his video “El extraño dibujo de la inteligencia artificial” transmit the idea that is like when you request to a child to draw something bases in his imaginations.
The Neural Networks is just one algorithm, and have its beginnings with “The Perceptron”, one algorithm that was invented in 1957 at the Cornell Aeronautical Laboratory by Frank Rosenblatt, and by 1958 The New York Times reported the perceptron to be “the embryo of an electronic computer that expects will be able to walk, talk, see, write, reproduce itself and be conscious of its existence.”

The concept of a demoniac AI that try to kill the humanity is good for a movie villain, but in the real world is far away of it, and the real danger in the AI is that every day we are leaving more and more responsibility to manage critical systems controlled by “dumb Intelligent Systems” with poor quality control and a deficient testing and homologation procedures.
Julian Bolivar-Galeno is an Information and Communications Technologies (ICT) Architect whose expertise is in telecommunications, security and embedded systems. He works in BolivarTech focused on decision making, leadership, management and execution of projects oriented to develop strong security algorithms, Artificial Intelligence (AI) research and its applicability to smart solutions at mobile and embedded technologies, always producing resilient and innovative applications.
The Artificial Intelligence is not Voodoo
2016/03/17
Encryption Is Foundational to The Future (Part 4 The Reign of the Electro-Mechanical Cyphers)

Until the 1950’s the WWII the ECM Mark II was used by the NATO, when it was replaced by machines like the KL-7.
KL-7 was an electro-mechanical rotor-based off-line cipher machine, developed by the National Security Agency (NSA) and was introduced in 1952 and served for many years as the main cipher machine of the US and NATO.
It is basically a more advanced version of the German Enigma machine, but the KL-7 has eight rotors, seven of which are moved in a complex irregular stepping pattern.
The machines came in several variations and were used by the US Army, Navy, NATO and Foreign Affairs for many years.

RACE (Rapid Automatic Cryptographic Equipment) is an off-line cipher machine, developed by Standard Telefon og Kabelfabrik A/S (STK) in Norway in the late 1970s, as one of the successors to the ageing KL-7.
RACE was the first high-end cipher machine were the cryptographic algorithms were purely implemented in software.
The algorithms were stored in PROMs and the machine was constructed in such a way that up to five algorithms plus a test-program could be installed, simply by adding banks of PROMs on one of the machine’s circuit boards.
Each algorithm, or PROGRAM as it was called, could be selected from the 6-position PROGRAM SELECTOR at the front panel.

DERBY was the Norwegian national CEROFF standard, which is similar to but not compatible with EPSOM. Is was probably only released to the Norwegian Armed Forces and national organisations. It supports two cryptografic keys, each of which provides full message protection, with special features for exclusive messages. It was approved by NATO for all levels of classification.
ASCOT is a special program for man-to-machine and machine-to-man communication. It allows the use of One-Time Pads (OTP) or the interoperable pocket size PACE encryptor at the other end. ASCOT was also released to foreign RACE customers.
EDITA was the so-called EDIT ASSISTENT that was developed to help the operator when preparing a punched message tape for ON-LINE transmission. EDITA was also released to foreign users.
Although the KL-51 was developed during the early 1980s, some units were still in use in the late 2000s. In 2006, the US Navy was developing plans to gradually replace the remaining KL-51 units with a more modern device that could be integrated with the latest complex data networks; a possible candidate for this replacement is the KIV-7.

The machine is similar to the American Sigaba, the KL-7 and the Enigma.
The original M-125 was succeeded by the M-125-3 in the mid-1960s and remained in use until the early 1990s.
At the heart of each Fialka machine is a drum with 10 different electromechanical cipher wheels or rotors, that move in an irregular manner when entering a message. Each wheel has 30 contacts at either side and is identified by a letter of the Russian alphabet.
The M-105, codename: AGAT, was a Russian off-line cipher machine that was developed and built in the USSR in the late 1960s. The machines were used by all countries of the Warsaw Pact and the encryption is due by a built-in key tape mixer that was fed with an 11-level punched paper tape with random data.
The M-105 was succeeded by the fully electronic M-205 D in 1986 but many M-105 machines remained in use until the end of the East-Germany. For communication between the East-Germany Government and Hungary, the M-105 was replaced by the T-353 (Dudek) in 1987.
Julian Bolivar-Galeno is an Information and Communications Technologies (ICT) Architect whose expertise is in telecommunications, security and embedded systems. He works in BolivarTech focused on decision making, leadership, management and execution of projects oriented to develop strong security algorithms, Artificial Intelligence (AI) research and its applicability to smart solutions at mobile and embedded technologies, always producing resilient and innovative applications.
Encryption Is Foundational to The Future (Part 4 The Reign of the Electro-Mechanical Cyphers)
2016/03/12
NeuroBrain, In a Small Introduction to Deep Machine Learning.

In this video you have a small example how machine learning really looks.
NeuroBrain is a self-structuring and evolutionary Recursive Neural Network (SSERNN) developed by BolivarTech, it has the ability to define it internal topology by itself during the learning process, by aggregating new structures when it is needed in order to learn a knowledge or pattern, and removing the unused ones when are not needed; just like a biological brain.
Also it has the evolutionary support that allow the use of BolivarTech’s evolutionary algorithms implementation, where using the crossing between individuals and mutations through generations of NeuroBrains populations, allow search and find optimal and semi-optimal topologies that can learn in a more efficient way the knowledge; just like occurs in the natural environment as was described by Charles Darwin, where the more adapted to an environment pass it abilities to the next generations.
The use of the innovative Self-Structuring and the Evolutionary algorithms allow to NeuroBrains be a powerful deep machine learning solution.
In the example show in the video, is a population of NeuroBrains and over generations and generations perform TicTacToe match between them in order to learn and find strategies to win the game.
Several match are at the same time, everyone with their own competitors in order to use the CPU multi core support.
Julian Bolivar-Galeno is an Information and Communications Technologies (ICT) Architect whose expertise is in telecommunications, security and embedded systems. He works in BolivarTech focused on decision making, leadership, management and execution of projects oriented to develop strong security algorithms, Artificial Intelligence (AI) research and its applicability to smart solutions at mobile and embedded technologies, always producing resilient and innovative applications.
NeuroBrain, In a Small Introduction to Deep Machine Learning.
2016/03/03
Encryption Is Foundational to The Future (Part 3 The Begin of the Technological Age)

The Enigma machine was developed by a German Arthur Scherbius in 1918 and was patented in 1919. It was marketed with portability and confidentiality as it sales features, but it had a lack of commercial success. When Germany discovered that they had lost WW I as a result of their cipher having been cracked by the British, despite the high cost, the machine was adopted by the German Navy in 1926, the Army in 1928 and the Air Force in 1935; also it was introduced into service with other sections of the German government.
The Enigma was an Off Line cipher system which was designed to provide high-grade cipher-text from the input of plaintext and the reverse.
The ciphering method used by Enigma is known as a polyalphabetic substitution cipher, and the “key” consists of a combination of gear wheels (rotors), known as “a scrambler”, on each of which 26 letters of the modern alphabet are inscribed, and a mechanism known as the plug-board for performing single character substitutions.
Enigma is used by first setting the scrambler and then typing the plain (unencrypted) text on the keyboard, the ciphered letters, encrypted by the scrambler, are displayed on a lamp board and this letter was transcribed on a message pad. A single scale is rotated by the scrambler each time a character is typed, which means that a different key is used to cipher every single character, the procedure repeated until the message was complete and the cypher-text message was then transmitted by radio using Morse code
Enigma decodes encrypted messages when the same key that was used to prepare the ciphered message is used to decrypt it, and following the same procedure the cipher-text is typed letter by letter and the plaintext equivalent is displayed on the lamp board.
The Enigma was, in terms of its internal architecture, a swapping machine and, as such, two machines with equal configuration would give the same result; for example, “X” to get “C” or “C” to get “X”. This meant that once the “configuration” or “key” was found, all messages using that could be decrypted. There was no internal dynamic update of the key based on the message traffic or any other variable. In addition, keying X would never give X and this latter weakness was used to great effect when applied to known text that provide clues to breaking a cipher-text containing for example expressions such as “Dear Sir”, or “Heil Hitler!”
Japanese Naval Code JN-25 was a secret-key substitution cipher where the cipher-text words appears as a number.
The cipher-text is generated by two other code groups, the first one assigned to the word a constant hard mapping of a unique 5 decimal digit numbers. For example.
Code group | Word |
41712 | Like |
64479 | You |
72084 | I |
80514 | Eat |
95280 | bananas |
39318 | apples |
The Second code group for a word consist of an “additive book” of code groups, determined by an “indicator” in the cipher-text, and added to the word’s own code group by no-carry addition.
For example, the additive group can be.
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
49356 | 70122 | 84213 | 69006 | 22242 | 92355 | 06150 |
To encode the message “I eat apples” and choose the indicator 4 is transformed in follow operation
| Message as code groups | 72084 | 80514 | 39318 |
| Additive groups, from 4 | 69006 | 22242 | 92355 |
| No-carry sums; ciphertext | 31080 | 02756 | 21663 |
Then the transmitted cipher-message is 4 31080 02756 21663
In order to recover the message only is necessary to calculate the subtraction between the ciphertext and the corresponding additive group.
During World War II, the US Navy developed a cipher machine, the Electronic Code Machine (ECM) Mark II, also known as SIGABA.
The ECM Mark II, had its roots in the “M-134”, a cipher machine designed by William Friedman before the war, and in fact the SIGABA was also known as the “M-134C”.
The original M-134 was conceptually similar to the Enigma in that it used a rotor system to scramble letters, but it differed in that it had five rotors, not three, and in that the rotors advanced in a seemingly random fashion, not in a nice neat progression with each character entered.
The movement of the rotors was controlled by a “paper tape”, which was a long strip of paper with holes punched across its width. In this case, the paper tape would accommodate five holes across its width, with a hole punched mean that the corresponding rotor must to advance, if no hole was punched, the rotor would not advance. Which hole controlled which rotor was determined by a plugboard with five plugs.
Given a long and properly devised paper tape, the sequence of rotor movements could be difficult to reverse-engineer. However, the paper tape produced operational issues, and Frank Rowlett used a separate set of rotors to generate the unpredictable sequence of rotor movements.
Friedman and Rowlett implemented this idea with a device called the M-229, which was connected to the M-134 in place of the paper-tape system.
The M-229 had three rotors of its own and a switch to vary its operation, and its output controlled the movement of the five rotors of the M-134.

The Soviet archives relating to signals intelligence are closed and information on cryptography is hard to find and verify, both during the Tsarist era and in the Soviet period.
Anatoly Klepov, a professional in the field of communications security has published “Encryptors and Radio Intelligence. Shield and Sword of Information World”, although the book was written for a Russian audience the author has published an interesting summary in English at aklepov.com ; and based on it we know “before the war in 1941 top secret information was encrypted with paper encryption documents” and “What was the way the USSR produced encryption keys before 1941?, They used special devices to generate keys to encryption equipment and one-time pads. The devices resembled modern Bingo game machine. The machine featured two units running punch tape. Balls randomly touched the punch tapes generating balanced gamma – random number sequence that was used to generate encryption key. The strength of such encryption keys was miserable.”
Julian Bolivar-Galeno is an Information and Communications Technologies (ICT) Architect whose expertise is in telecommunications, security and embedded systems. He works in BolivarTech focused on decision making, leadership, management and execution of projects oriented to develop strong security algorithms, Artificial Intelligence (AI) research and its applicability to smart solutions at mobile and embedded technologies, always producing resilient and innovative applications.
Encryption Is Foundational to The Future (Part 3 The Begin of the Technological Age)
2016/02/25
Encryption Is Foundational to The Future (Part 2 The Century of Huge Advances)

At the begin of the 20th century, cryptography was a labor intensive, error prone process, capable of transforming a small amount of written material into an encoded cipher text form.
With the advancement of communication technology, encryption and decryption came to be actively performed during World War I.
On the first day of hostilities of the World War I, the British cable ship Telconia located and cut Germany’s transatlantic cables, forcing them to send all their international traffic via Sweden, American cables or wireless communications, and the German forces then started to encrypt their communications in an attempt to prevent hostile countries from reading them, but soon all German traffic was routinely routed to Room 40, the Royal Navy’s cypher organization.

Towards the end of WWI the head of cryptographic research for the US Army Major Joseph Mauborgne introduced the concept of a code based on truly RANDOM keys. This would take the form of two identical pads printed with lines of randomly generated letters. Using the Vigenere technique, each page is to be used to encrypt and decrypt ONE message and then destroyed; introducing the concept of the one use key.
The weakness of the Vigenere square was the repetition of the key. This new technique injected the same randomness into the cyphertext as was contained in the key and there was therefore no useable pattern or structure within the message. Attacks seeking to exploit these weaknesses such as the Babbage and Kasiski tests, would fail.

This method is still in use today, called the One Time Letter Pad or OTLP, and is used for encrypting the most secret of communications. OTLP is still the only ‘admitted’ system to provide the ‘holy grail’ of cryptography of perfect secrecy.
Julian Bolivar-Galeno is an Information and Communications Technologies (ICT) Architect whose expertise is in telecommunications, security and embedded systems. He works in BolivarTech focused on decision making, leadership, management and execution of projects oriented to develop strong security algorithms, artificial intelligence (AI) research and its applicability to smart solutions at mobile and embedded technologies, always producing resilient and innovative applications.
Encryption Is Foundational to The Future (Part 2 The Century of Huge Advances)
2016/02/23
You are the Social Networks' Product...
 Facebook, Twitter and other social networks expose your personal information far beyond your group of friends and remember that really you are not customers of them, you’re their product.
Facebook, Twitter and other social networks expose your personal information far beyond your group of friends and remember that really you are not customers of them, you’re their product.
Users need to remember that the Social Networks makes money from its advertisers, not from the users; and the advertisers want to get their message out to as many people as possible; because this fact, they share your information to everyone, not just your “friends”; and most recently for example Facebook’s facial recognition technology automatically suggests that friends tag you, unless you turn it off.
The most popular scams on social networks include cross-site scripting, clickjacking, survey scams and identity theft, but far from this technical breach, we are our first security hole.

We publish everything from our day to day activities, leaving a virtual trail of breadcrumbs about our behavior, what we like and dislike, our way to think and watch the world and more important when and where we do all of our things and our relationship with others in our environment; and there is the social networks’ business, they collect (and we are happy to provide it) and process and catalog all our information and they sell it in a direct way to organizations, governmental and private agencies, and in an indirect way when publicity is included in the social networks’ site.
I remember one time my best friend told me, “If I am not capable to keep my own secrets how I will demand to other to keep it”, and this is a big true at the social networks; we published our private life without fear, and really is a good thing that there are certain ethical restrictions because otherwise I do not even want to imagine the things would be published without any shyness.
 At Valhala Networks and all the information security professionals in general, work hard to keep your information safe, but our efforts are futile without the final user awareness about his own privacy.
At Valhala Networks and all the information security professionals in general, work hard to keep your information safe, but our efforts are futile without the final user awareness about his own privacy.
My free advice as security consultor, please think twice about the consequences before publish anything in a social network because the internet don’t forget and just remember, “Do not be fooled, if you do not pay for the product, then the product is you !!!”
Julian Bolivar-Galeno is an Information and Communications Technologies (ICT) Architect whose expertise is in telecommunications, security and embedded systems. He works in BolivarTech focused on decision making, leadership, management and execution of projects oriented to develop strong security algorithms, artificial intelligence (AI) research and its applicability to smart solutions at mobile and embedded technologies, always producing resilient and innovative applications.
You are the Social Networks' Product...
BlackEnergy and Stuxnet the first Cyber Weapons on a Global Cyberwarfare
 Western Ukraine power company Prykarpattyaoblenergo reported an outage on December 23 2015, saying the area affected included regional capital Ivano-Frankivsk, with a population of 1.4 million, during few hours.
Western Ukraine power company Prykarpattyaoblenergo reported an outage on December 23 2015, saying the area affected included regional capital Ivano-Frankivsk, with a population of 1.4 million, during few hours.
Now at January 2016, the researchers have proof that link that outage with the malware called BlackEnergy.
BlackEnergy is a popular malware that is sold in the Russian cyber underground and dates back to early as 2007.
Originally, it was designed as a toolkit for creating botnets for use in conducting Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks; but over the time has evolved to support different plugins, which are used to extend its capabilities to provide necessary functions, depending on the purpose of an attack.
The BlackEnergy toolkit capabilities has been used by different gangs for different purposes like sending spam, stealing banking credentials; but the most notorious use may be when it was used to conduct cyberattacks against Georgia during the Russo-Georgian confrontation in 2008, also at the summer of 2014, BlackEnergy was tailored by plugins to target Ukrainian government institutions.
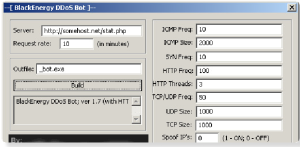
The BlackEnergy toolkit comes with a builder application which is used to generate the clients that the attackers use to infect victim machines; also it comes with server-side scripts, which the attackers set up in the Command and Control (C&C) server. The scripts also provide an interface where an attacker can control his bots. The simplicity and convenience provided by this toolkit means that anyone who has access to the kit can build his own botnet without any skills required, and how was demonstrated by the Ukraine power grid attack it can be easily converted in a cyber weapon.
In order to do the Ukraine power outage was used the BlackEnergy’s trojan, together with a backdoored SSH server introduced in the targets’ system and the destructive KillDisk plugin, which were all detected in several electricity distribution companies in Ukraine, are a dangerous set of malicious tools used as cyber weapon that give the attackers remote access to the company’s network and the capability of shutting down critical systems and by wiping their data, making it harder to get them up and running again.
But how is possible that “standard” malware can infect specialized industrial software?

It’s common, in order to reduce cost and time, that dedicated software used to program and control industrial hardware will run on PCs with operating systems like Windows or Linux; and these can then be targeted using similar or even the same malware that is used to attack regular internet users; and also all the regular vectors of attack can be used, including human error and social engineering.
Another very serious risk is to connect industrial systems to the internet, but based on my expertise this practice is common due to practicality and cost savings, because in order to reduce the number of high level trained employees is allowing to the existent ones to access the system remotely and solve any problem in an expedite way.
This factors of integrating commercial solutions and internet connection exposes the industrial control system to the same threats that common PCs face, but with much fewer options for defense because for example, software patching is much more problematic with industrial systems because they tend to be heavily customized and they are often always on, and in order to perform a maintenance it must be very well planned.
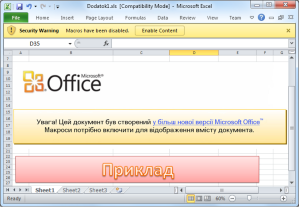
At the Ukraine power attack, the vector used was to convince the user to execute a malicious macro in Microsoft Office files. In this case no vulnerability is used to try to infect system, just trying to trick the user to execute the malicious macro.
But BlackEnergy is not the first cyber weapon known because at January 2010, the most sophisticated cyber weapon the world had ever seen, ravaged the Iran’s nuclear program.
This malware dubbed Stuxnet, was allegedly developed by the U.S. and Israel to infect the Natanz uranium enrichment plant in Iran, the complex virus infected the computer system that ran the centrifuges and making slight tweaks to the software caused hundreds of the centrifuges to self-destruct.

Stuxnet was designed to manipulate computer systems made by the German firm Siemens that control and monitor the speed of the centrifuges. The attack was due by infecting the Step 7 project files used to program Siemens’ PLCs.
The computers at Natanz are disconnected from the internet and cannot be reached directly by the remote attackers. Because this Stuxnet was designed to spread via infected USB flash drives using the Windows Autorun feature or through the victim’s local network using the print-spooler zero-day exploit that Kaspersky Lab and Symantec later found in the code.
In order to Stuxnet reach its target machines, the attackers first infect computers belonging to five outside companies that are believed to be connected in some way to the nuclear program. Then employees from this companies become an unwitting courier who will help spread and transport the weapon on flash drives into the protected facility and the Siemens computers at the end.
It’s not clear how long it took Stuxnet to reach its target after infecting machines in the contractor companies.
According to one U.S. intelligence source, Stuxnet’s developers tried to deploy a version of the Stuxnet malware to attack North Korea’s nuclear weapons.
This malware would be activated when it encountered Korean-language settings on an infected machine.

The attackers could not access the core machines that ran Pyongyang’s nuclear weapons program as was at Iran, and tried to deploy it using the same vector attack; but ultimately this attempt failed because in contrast to Iranians that access the Internet broadly and had interactions with companies from around the globe; North Korea has some of the most isolated communications networks in the world, where just owning a computer requires police permission, and the open Internet is unknown except to a tiny elite. Also the country has one main conduit for Internet connections to the outside world, through China allowing the complete control over the information that pass-through it.
The advantage that custom-made have over a weaponized public-domain malware, reside in the firsts are more difficult or impossible to detect by commercial antivirus because the limited and targeted objectives prevent to this companies get samples to be incorporated in their solutions before the attack was did. But the use of public domain malware for politically-oriented attack is an intriguing convergence of criminal activity and espionage, because as the kit is being used by multiple criminal groups, it provides a greater measure of plausible deniability than is afforded by a custom-made piece of code.
Julian Bolivar-Galeno is an Information and Communications Technologies (ICT) Architect whose expertise is in telecommunications, security and embedded systems. He works in BolivarTech focused on decision making, leadership, management and execution of projects oriented to develop strong security algorithms, artificial intelligence (AI) research and its applicability to smart solutions at mobile and embedded technologies, always producing resilient and innovative applications.
BlackEnergy and Stuxnet the first Cyber Weapons on a Global Cyberwarfare
NSA Believe that Current Cryptography Algorithms Are Broken by New Quantum Computers
 Quantum computing is a new way to build computers that takes advantage of the quantum properties of particles to perform operations on data in a very different way than traditional computers.
Quantum computing is a new way to build computers that takes advantage of the quantum properties of particles to perform operations on data in a very different way than traditional computers.
With this computational performance improvement came other risks, and more in the cryptography area where the security resides in apply to the plain data mathematical operations hard to replicate in a reasonable time without the knowledge of specific parameters values.
At quantum computers exist the Shor’s algorithm and the Minimization algorithm can efficiently factor numbers and can break RSA, Diffie-Hellman and other discrete log-based cryptosystems, including those that use elliptic curves.

The Shor’s algorithm is composed of two parts. The first part of the algorithm turns the factoring problem into the problem of finding the period of a function, and may be implemented classically. The second part finds the period using the quantum Fourier transform, and is responsible for the quantum speedup.
Minimization algorithm relies on first transforming the factorization problem into an optimization problem and as was exposed at my other article “Quantum Computers are already here? “, at the level of the machine, the actual quantum processor solves a Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization problems that can provide faster ways to get optimal and semi-optimal results.

Before have panic and declare that internet security is broken, we need to know using these algorithms the largest such number that we found without using any prior knowledge of the solution to the factorization problem was 56153, that is 16 bits, using only 4 qubits; in order to exploit the true power of quantum mechanics in this type of computation, finding the solution will need to make use of more qubits and remember that D-Wave 2X have 1000 qubits available to be used in the quantum processor.
In August 2015, the U.S. government’s National Security Agency (NSA) released a major policy statement on the need to develop standards for post-quantum cryptography (PQC).
 In this announcement, the NSA explain about his intentions to “initiate a transition to quantum resistant algorithms in the not too distant future” and also recommend “for those partners and vendors that have not yet made the transition to Suite B elliptic curve algorithms, we recommend not making a significant expenditure to do so at this point but instead to prepare for the upcoming quantum resistant algorithm transition.”
In this announcement, the NSA explain about his intentions to “initiate a transition to quantum resistant algorithms in the not too distant future” and also recommend “for those partners and vendors that have not yet made the transition to Suite B elliptic curve algorithms, we recommend not making a significant expenditure to do so at this point but instead to prepare for the upcoming quantum resistant algorithm transition.”
NSA Suite B Cryptography is a set of cryptographic algorithms promulgated as part of its Cryptographic Modernization Program; and It is to serve as an interoperable cryptographic base for both unclassified information and most classified information.
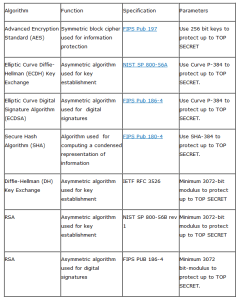
NSA Suite A Cryptography is a cryptography category which contains classified algorithms that will not be released and will be used for the protection of some categories of especially sensitive information.
Also the NSA recommend “for those customers who are looking for mitigations to perform while the new algorithm suite is developed and implemented into products”, “first, it is prudent to use larger key sizes in algorithms in many systems”; additionally, when “using layered commercial solutions to protect classified national security information with a long intelligence life should begin implementing a layer of quantum resistant protection. Such protection may be implemented today through the use of large symmetric keys and specific secure protocol standards”.
Symmetric-key encryption schemes such as AES have the property that the fastest quantum attack known for recovering a k-bit secret key takes time 2^k/2. Thus AES with 256-bit keys is believed to provide a 128-bit security level against quantum attacks, that is half the number of bits of security that it has against conventional attacks.

At Valhala Networks to secure our documents, electronic schemas and source codes we use CuaimaCrypt that is a Symmetric-key encryption algorithm and based in a theoretical (we don’t have access to a quantum computer) pre-evaluation it is quantum resilient because it dynamic structure, number of equivalent bits and algorithm’s operation.
You can use it free just downloading the “CuaimaCrypt Command Line” or CCLI from the Valhala’s web site.
Other viable candidates for postquantum cryptography can be Lattice-based cryptography that are being intensively studied by cryptographers, because they can be used to achieve fully homomorphic encryption and code obfuscation not known to be achievable using conventional RSA and discrete logarithm cryptography.

Hash-based cryptography, because is believed to have the same security against quantum computers as against conventional ones, k/2 bits of security, where k is the bit length of hash values.
Multivariate polynomial cryptography, where the security of these schemes is based on the difficulty of solving a multivariate system of polynomial equations over a finite field.
Isogeny-based cryptography, where the security of these schemes is based on the difficulty of computing an isogeny of a certain degree between two isogenous super-singular elliptic curves over Fp2
We must note that this post PQC algorithms don’t have any relation with Quantum Cryptography

Quantum Cryptography is essentially based on the usage of individual particles/waves of light (photon) over a transmission channel and their intrinsic quantum properties know as Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle to develop an unbreakable cryptosystem because it is impossible to measure the quantum state of any system without disturbing that system.
It is theoretically possible that other particles could be used, but photons offer all the necessary qualities needed, their behavior is comparatively well-understood.
Also the actual commercial quantum cryptography is used in quantum key distribution systems over fiber channels.
In conclusion I don’t think that internet security is actually broken, but the certain is, based on the actual quantum computer’s development state, in few years “we will be short” at the quantity of bits used by current cryptographic algorithms and we need to take care of this possibility from now because after will be late.
Julian Bolivar-Galeno is an Information and Communications Technologies (ICT) Architect whose expertise is in telecommunications, security and embedded systems. He works in BolivarTech focused on decision making, leadership, management and execution of projects oriented to develop strong security algorithms, artificial intelligence (AI) research and its applicability to smart solutions at mobile and embedded technologies, always producing resilient and innovative applications.
NSA Believe that Current Cryptography Algorithms Are Broken by New Quantum Computers
Quantum Computers are Already Here?
 We have years with the promise of a commercial quantum computer will be developed to solve complex problems at unprecedented speeds. But appear that “the future is now” with the first generation of commercial quantum computers.
We have years with the promise of a commercial quantum computer will be developed to solve complex problems at unprecedented speeds. But appear that “the future is now” with the first generation of commercial quantum computers.
But first we need to establish what is and how work a quantum computer.
First in quantum computing, a qubit or quantum bit or qbit is a unit of quantum information, analogue of the classical bit.
A qubit is a two-state quantum-mechanical system, where the two states can be vertical and horizontal polarization for example, and this states are used to encode information as 0s, 1s or both simultaneously.
This “superposition” of states, along with the quantum effects of entanglement and quantum tunneling, enable quantum computers to consider and manipulate many combinations of bits simultaneously.
One of the problems with the actual Quantum computers is that need to be near to 0 Kelvins and shield from any electromagnetic and mechanical disturbance; this is in order to allow the quantum effects can play a role in computation, the quantum processor must operate in an extreme isolated environment with refrigeration and many layers of shielding in order to create an internal environment with a temperature close to absolute zero and that is isolated from external magnetic fields, vibration, and external RF signals of any form.
The actual commercial system implements a quantum annealing algorithm, which solves problems by searching for the global minimum of a function. This is fundamentally different from the familiar framework of classical computing built on logical operations, but it is relevant in many high value problems such as minimizing error for example in a voice recognition system, learning algorithms, break cryptographic symmetric keys, controlling risk in a financial portfolio, or reducing energy loss in an electrical grid, etc.
While there are different ways in which users can submit problems to the system, at the level of the machine instruction of the quantum processor the system solves a Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization Problem (QUBO), where binary variables are mapped to qubits and correlations between variables are mapped to couplings between qubits. The system of interacting qubits is evolved quantum mechanically via the annealing algorithm to find optimal or near-optimal solutions.
 Solving problems with a quantum system can be thought of as trying to find the lowest point on a landscape of peaks and valleys. Every possible solution is mapped to coordinates on the landscape, and the altitude of the landscape is the “energy’” or “cost” of the solution at that point. The aim is to find the lowest point or points on the map and read the coordinates, as this gives the lowest energy, or optimal solution to the problem.
Solving problems with a quantum system can be thought of as trying to find the lowest point on a landscape of peaks and valleys. Every possible solution is mapped to coordinates on the landscape, and the altitude of the landscape is the “energy’” or “cost” of the solution at that point. The aim is to find the lowest point or points on the map and read the coordinates, as this gives the lowest energy, or optimal solution to the problem.
The special properties of quantum physics, such as quantum tunneling, allow the quantum computer to explore this landscape in ways that have never before been possible with classical systems. Quantum tunneling is like a layer of water that covers the entire landscape. As well as running over the surface, water can tunnel through the mountains as it looks for the lowest valley. The water is an analogy for the probability that a given solution will be returned. When the quantum computations occur, the “water” or probability is pooled around the lowest valleys. The more water in a valley, the higher the probability of that solution being returned. A classical computer, on the other hand, is like a single traveler exploring the surface of a landscape one point at a time.
Founded in 1999, D-Wave Systems is a quantum computing company that makes quantum processors based on superconducting circuits. They last processor the D-Wave 2X, with 1000 qubits, can evaluate all 21000 possible solutions at the same time.
 The physical footprint of the D-Wave 2X is approximately 10’ x 7’ x 10’ (L x W x H) where It houses a cryogenic refrigeration system, shielding and I/O systems that support a single thumbnail-sized quantum processor. Most of the physical volume of the current system is due to the size of the refrigeration system. The adjoining cabinets contain the control subsystems and the front-end servers that provide connectivity to the system.
The physical footprint of the D-Wave 2X is approximately 10’ x 7’ x 10’ (L x W x H) where It houses a cryogenic refrigeration system, shielding and I/O systems that support a single thumbnail-sized quantum processor. Most of the physical volume of the current system is due to the size of the refrigeration system. The adjoining cabinets contain the control subsystems and the front-end servers that provide connectivity to the system.
The D-Wave 2X system can be deployed as part of a High Performance Computing (HPC) data center using standard interfaces and protocols.
The I/O subsystem is responsible for passing information from the user to the processor and back. After receiving a problem from the user via standard web protocols, data is converted to analog signals and carried on normal conducting wires that transition to superconducting wires at low temperatures.
The only path for signals between the inside and outside of the shielded enclosure is a digital optical channel carrying programming information in, and results of computations out.
The processor resides in a high vacuum environment in which the pressure is 10 billion times lower than atmospheric pressure, temperature of 15 millikelvin, which is approximately 180 times colder than interstellar space, and the magnetic shielding subsystem achieves fields less than 1 nanotesla across the processor in each axis witch is approximately 50000 times less than the Earth’s magnetic field.
Some researchers think that the D-Wave 2X is not a quantum computer, is just a quantum annealer, which is only a part of a computer. The annealer’s role is to specify interactions for its qubits so they can find the lowest energy states.
After read the papers about how work and program a D-Wave 2X computer is easy to understand that computer is not a general use computer, you can’t expect go to buy a quantum version of the universal processor in your PC and play a game at quantum speeds. The D-Wave 2X design is to solve a very specific problem of find the global minimum value of a very complicated function and cannot be programmed to perform a range of tasks.
At this moment at quantum computer technology we are at the same level had by binary computers during the World War II when only can solve specific problems about projectile’s ballistic calculus or the Turing’s machine to break the Enigma code.
In conclusion my opinion and with these technical facts in mind is possible infer that we are a few decades away to create a quantum universal processor.
Julian Bolivar-Galeno is an Information and Communications Technologies (ICT) Architect whose expertise is in telecommunications, security and embedded systems. He works in BolivarTech focused on decision making, leadership, management and execution of projects oriented to develop strong security algorithms, artificial intelligence (AI) research and its applicability to smart solutions at mobile and embedded technologies, always producing resilient and innovative applications.
Quantum Computers are Already Here?
Malfeasance by Cheatware
 During the past six years, Volkswagen was cheating on the emissions testing for its diesel cars because the cars’ computers were able to detect when they were being tested, and temporarily alter how their engines worked so they looked much cleaner than they actually were and when they weren’t being tested, the car produced 40 times more the pollutants.
During the past six years, Volkswagen was cheating on the emissions testing for its diesel cars because the cars’ computers were able to detect when they were being tested, and temporarily alter how their engines worked so they looked much cleaner than they actually were and when they weren’t being tested, the car produced 40 times more the pollutants.
Computers allow people new ways to cheat, because the cheating is at the embedded software and the malicious actions only happen when the expected conditions are presented, otherwise continue with the normal operation mode. Because the software is “smart” in ways that normal objects are not, the cheating can be subtle and harder to detect.
The Internet of Things is supposed coming and many industries are moving to add embedded computers to their devices, and that will bring with it new opportunities for manufacturers to cheat; for example, light bulbs could appear more energy efficient than they are, temperature sensors could do appear that food has been stored at safer temperatures than it has been, voting machines could appear to work perfectly, except during the presidential polls date, when they undetectably switch a few percent of votes from one party’s candidates to another’s, electricity meters add some cents more to the measure, etc.
This cheating embedded software won’t be solved through as standards computer security procedures, because they are designed to prevent outside hackers from breaking into your computers and networks. The car’s analogue example would be security software that prevented an owner from tweaking his own engine to run faster but in the process emit more pollutants; the real task is contend malfeasance programmed in at the design stage.

Software verification has two parts, transparency and oversight. Where transparency means making the source code available for analysis by independent investigators. The need for this is obvious because it’s much easier to hide cheating software if a manufacturer can hide the code. Oversight means that analysis can’t be limited to a once-every-few-years government test; is necessary private analysis as well.
Both transparency and oversight are not accomplished in the right way at the software world because companies routinely fight making their code public and attempt to muzzle independent security researchers who find problems, citing the proprietary nature of the software; really it’s a fair complaint, but the public interests of accuracy and safety need to be more that business interests.
Proprietary software is widely being used in critical applications like voting machines, medical devices, breathalyzers, electric power distribution, etc. And as I said at my other article “Artificial Intelligence, is really so dangerous?” we’re ceding more control of our life to “dumb Intelligent Systems” with poor quality control and a deficient testing and homologation procedures; but overall software quality is so bad that products ship with thousands of programming mistakes and most of them don’t affect normal operations, this is why your software generally works just fine; but some of them do and is why your software occasionally fails, and needs constant updates. By making cheating software appear to be a programming mistake, the cheating looks like an accident and unfortunately this type of deniable cheating is easier than people think.

Malfeasance by software is easier to commit and harder to prove because fewer people need to know about the conspiracy, and it can be done in advance and far to the testing time and homologation; and, if the “cheatware” remains undetected for long enough, it could easily be the case that no one in the company know that it’s there.
From the companies’ point of view and also for me as software developer, I can understand that software algorithms are a time and money investment in development and research, and can be the most precious (or the only one) asset of the company, and publish the source code is like request to Coca-Cola or Pepsi reveal his soda recipes; also I know that often the project’s schedule and money investments are against to perform a meticulous software auditory.
In one side we have that transparency and oversight is the only way verify that software is doing the job as expected and at the other side the right to protect intellectual property, and the midway between both situations the more viable option would be that companies follow procedures to receive certifications by external entities for his software, and a contract to provide a non-disclosure agreement about the source code but allow a full release of the tests, procedures and results by the external certification entity.
In conclusion we need a better verification of the software that controls our lives in this modern world, because can be the case when our lives will be depending of them.
Julian Bolivar-Galeno is an Information and Communications Technologies (ICT) Architect whose expertise is in telecommunications, security and embedded systems. He works in BolivarTech focused on decision making, leadership, management and execution of projects oriented to develop strong security algorithms, artificial intelligence (AI) research and its applicability to smart solutions at mobile and embedded technologies, always producing resilient and innovative applications.
Malfeasance by Cheatware
Now ‘iSpyU’ business is outsourcing
 From unmemorable times always the governments have trying to collect intelligence information about people problematic for them within same folks. But this always was an “in house business” where the own government develop itself tools and procedures to accomplish the task; until now when the ‘iSpyU’ business can be outsourced by anyone thanks to products like the FinFisher Suite.
From unmemorable times always the governments have trying to collect intelligence information about people problematic for them within same folks. But this always was an “in house business” where the own government develop itself tools and procedures to accomplish the task; until now when the ‘iSpyU’ business can be outsourced by anyone thanks to products like the FinFisher Suite.
FinFisher is a remote intrusion and surveillance software developed by Munich-based Gamma International GmbH and marketed and sold exclusively to law enforcement and intelligence agencies by the UK-based Gamma Group.

FinFisher is sold as a “lawful interception” suite for monitoring criminals, but it has gained notoriety because it has been used by repressive governments in targeted attacks against human rights campaigners and opposition activists in countries with questionable human rights records like Bahraini, Ethiopia, Serbia, Turkmenistan, Venezuela, Vietnam, etc.
The major information about FinFisher came from The Citizen Lab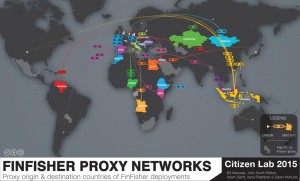 that is a laboratory based at the Munk School of Global Affairs, University of Toronto, Canada and it focus on advanced research and development at the intersection of Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs), human rights, and global security.
that is a laboratory based at the Munk School of Global Affairs, University of Toronto, Canada and it focus on advanced research and development at the intersection of Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs), human rights, and global security.
As information leaked and collected from the deep web “Spy your opponents” is not cheap, and the suggested “tag price” for FinFisher products (including a full set of attack software, booby-trapped thumb drives and nearly a dozen different training courses) retailed for some 3.5 million dollars (3 million Euros)
FinFisher provide the follow spy feature on target devices (computers, cellphones):
- Bypassing of 40 regularly tested Antivirus Systems
- Covert Communication with Headquarters
- Full communications monitoring (Calls, Video, Contact List, etc.)
- Recording of common communication like Email, Chats, Voice-over-IP, WhatsApp, Skype, SMS, Chats, File Transfers, etc.
- Live Surveillance through inbuilt camera and microphone
- Country Tracing of Target
- Silent extracting of Files from device
- Process-based Key-logger for faster analysis
- Live Remote Forensics on Target System
- Advanced Filters to record only important information
- Supports most common Operating Systems (Windows, Mac OSX, Linux, Android, iOS, Windows Phone)
For me as security specialist is curious ear how competitors propose to avoid this kind of surveillance focus to use encryption software, when the target device is compromised at the level to allow key-logger capabilities to capture what the user is typing from the source and file transfers directly from devices, any kind of encryption are useless because it is to protect against transmission media taped not compromised terminals.
To mitigate this kind of surveillance the only choices available is be very careful about software installed in your terminals because you can’t trust on your antivirus because can be easy bypassed; other more radical countermeasures are available for human rights campaigners and opposition activists who know that can be targets from oppressive governments.
Julian Bolivar-Galeno is an Information and Communications Technologies (ICT) Architect whose expertise is in telecommunications, security and embedded systems. He works in BolivarTech focused on decision making, leadership, management and execution of projects oriented to develop strong security algorithms, artificial intelligence (AI) research and its applicability to smart solutions at mobile and embedded technologies, always producing resilient and innovative applications.
Now ‘iSpyU’ business is outsourcing






